Top 10 Worst Fighter Jets In The World
Today we will tell you about the Top 10 Worst Fighter Jets In The World with Images, Specifications and you can download this Pdf with one click just go to the end of this article, Air Forces from both sides of World War II rapidly realized that jet fighters were entering a new weapons race as propeller-driven aircraft had hit their speed limit. Early designs frequently had problems because this was a new technology that was attempting to break the sound barrier without knowing how engines and airframes would respond to higher speeds and more stress mistakes would be made and Designs will not live up to expectations some of these have occurred more recently than you might think in this article we have selected the 10 Most Dangerous fighter jets ever made, So Let’s Start and Find out the List of Top 10 Worst Fighter Jets In The World.
Table of Contents
List of Top 10 Worst Fighter Jets In The World
The table provides the List of the Top 10 Worst Fighter Jets In The World along with their Types.
| Sl. No. | Jet Names | Cause |
| 10 | BAE Lightning | Blisteringly Quick, Heavy On Fuel |
| 9 | Messerschmitt Me-163 Komet | Fast And Deadly |
| 8 | Yakovlev Yak-38 | Soviet Answer To the Harrier |
| 7 | Convair F-102 Delta Dagger | Not Quite Supersonic |
| 6 | Heinkel He-162 | Plywood And Glue Construction For Home Builds |
| 5 | Vought F7U Cutlass | Underpowered And Unreliable |
| 4 | Bell P-59 Airacomet | Slower Than Piston Aircraft It Replaced |
| 3 | De Havilland Sea Vixen | Accidents Accounted For 38% Of All Aircraft |
| 2 | Mikoyan Gurevich Mig-23 | Still In Service 50 Years Later |
| 1 | Lockheed F-35 Lightning II | Failed To Meet Its Original Design Criteria |
World’s Top 10 Worst Fighter Jets
Now that you know World’s Top 10 Worst Fighter Jets with Specifications and Images, etc. So, let us learn a little bit more about them in detail.
10. BAE Lightning – Blisteringly Quick, Heavy On Fuel
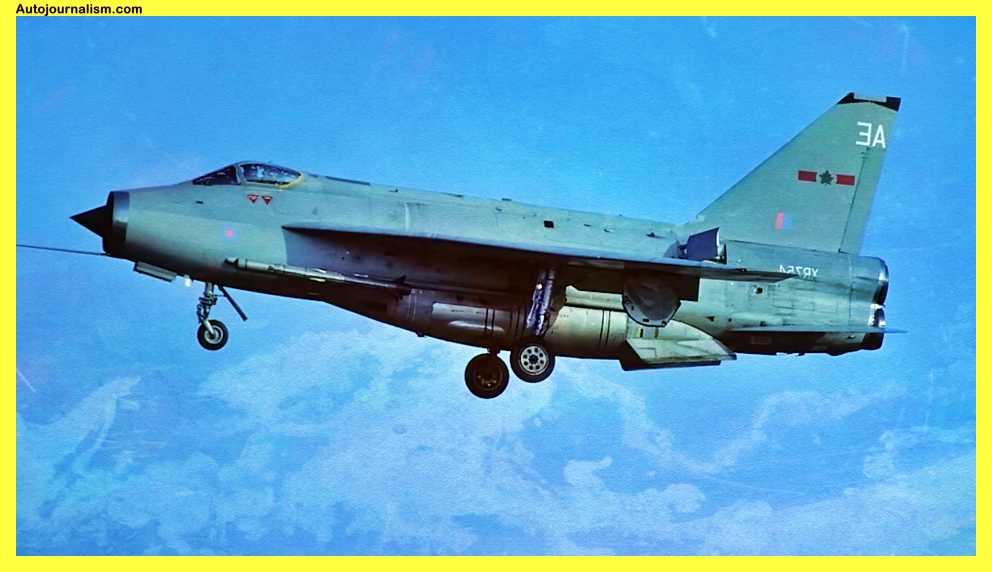

In contrast to other fast jet designs of the 1960s and 1970s, Britain’s rapid reaction Interceptor, the Bae Lightning, was a full-fledged indigenous product capable of exceeding 1,500 miles per hour performance. The Lightning’s incredible 20,000 feet per minute rate of travel topping out at altitudes exceeding 60,000 feet was by far the most impressive Display of Power, but all that power and performance came at a cost with limited internal fuel and a battle radius of only 150 miles later. The Bae lightning variants with their annoying overwing tanks sacrificed performance for range with a top speed.
Here are some key specifications for the BAE Lightning:
- Length: 54 ft 4 in (16.56 m)
- Wingspan: 31 ft 9 in (9.68 m)
- Height: 16 ft 6 in (5.03 m)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 41,000 lb (18,597 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Rolls-Royce Avon 202 turbojets, 16,100 lbf (71.8 kN) each
- Maximum speed: 1,300 mph (2,092 km/h)
- Range: 1,150 mi (1,850 km)
- Service ceiling: 55,000 ft (16,764 m)
- Armament: 2 × 30 mm ADEN cannon, up to 8,000 lb (3,629 kg) of bombs, missiles, or rocket pods
It should be noted that these specifications may vary slightly depending on the specific model of the BAE Lightning.
9. Messerschmitt Me-163 Komet – Fast And Deadly
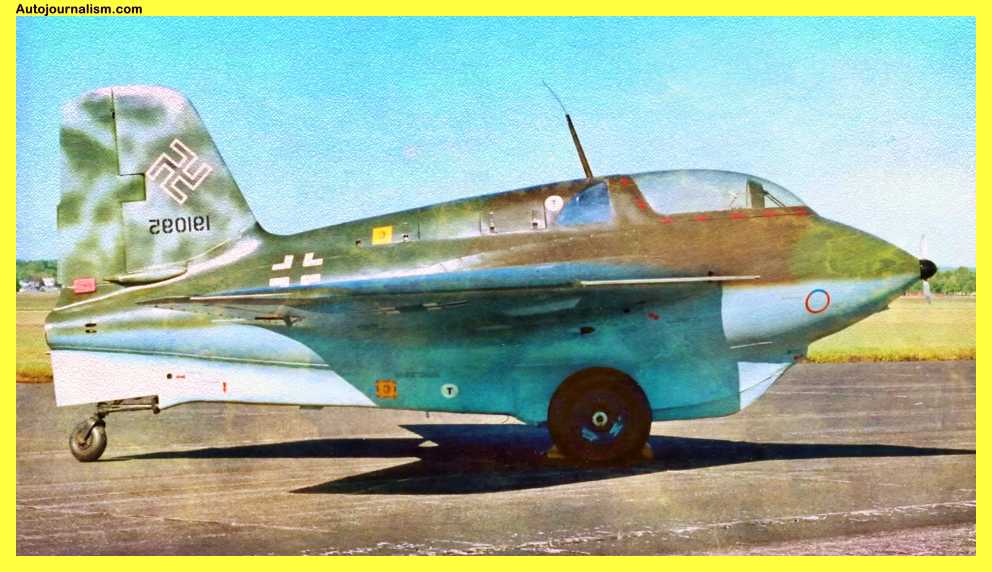

Germany displayed the me-163 comet, a step forward, in need of a quick air defense fighter but without a jet engine that wouldn’t arrive for another two years. Mesa Since highly corrosive hydrogen peroxide and methanol hydrazine would melt human flesh upon contact, Schmidt outfitted the comet with a Walter hwk 109 rocket motor, giving Pilots a potential top speed of 650 miles per hour before climbing to their operational height and gliding back to land. This made the me163 a deadly place to be.
The Messerschmitt Me-163 Komet was a German rocket-powered interceptor aircraft used by the Luftwaffe during World War II. It was the first rocket-powered fighter aircraft to see operational use and was known for its high speed and unusual design. Here are some key specifications for the Me-163:
- Length: 14.5 m (47 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 6.7 m (22 ft 0 in)
- Height: 3.4 m (11 ft 2 in)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 3,730 kg (8,223 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Walter HWK 109-509A liquid-fueled rocket engine, 7.8 kN (1,750 lbf) of thrust
- Maximum speed: 1,130 km/h (700 mph)
- Range: 16–25 minutes of powered flight
- Service ceiling: 12,000 m (39,370 ft)
- Armament: 2 × 30 mm (1.18 in) Rheinmetall-Borsig MK 108 cannon, mounted in the nose
It should be noted that the Me-163 was not a practical aircraft due to its short range and high fuel consumption. It saw limited use in the final months of World War II and was not a significant factor in the outcome of the war.
8. Yakovlev Yak-38 – Soviet Answer To The Harrier
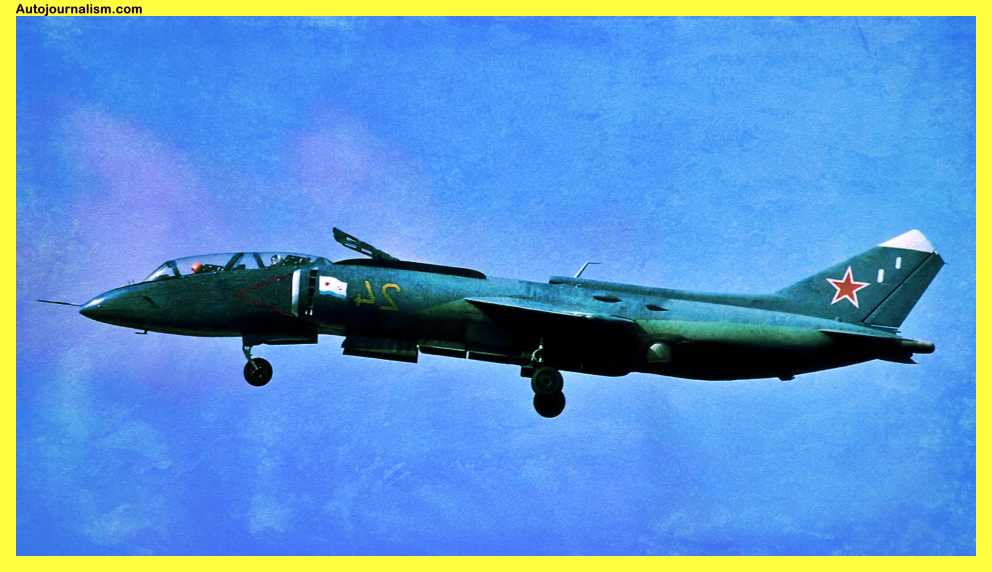

If you look closely, you can see how the yak-38 was affected by hair wear, but unlike the West, Yakov Lev’s Engineers never advanced quite as far. In addition, certain yak-38 issues were from the aircraft being hurried into service despite being faster than the Harrier, Because it had a shorter range than the hairier and was famously difficult for beginning pilots to fly, it had less appeal. Yakov Levy employed a twin-engine design to enable the plane to travel faster than the speed of sound, but this created more issues than it resolved because the plane would typically crash if one engine failed.
The Yakovlev Yak-38 (NATO reporting name: “Forger”) was a Soviet naval VTOL (Vertical Takeoff and Landing) aircraft developed in the 1970s. It was designed as an answer to the British Hawker Siddeley Harrier, and was the Soviet Union’s only operational VTOL aircraft. Here are some key specifications for the Yak-38:
- Length: 14.5 m (47 ft 7 in)
- Wingspan: 8.0 m (26 ft 3 in)
- Height: 4.2 m (13 ft 9 in)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 11,000 kg (24,251 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Klimov RD-38 turbofan, 9,800 lbf (44 kN) of thrust
- Maximum speed: 915 km/h (517 mph)
- Range: 800 km (497 mi)
- Service ceiling: 14,500 m (47,600 ft)
- Armament: 2 × 30 mm NR-30 cannon, up to 1,000 kg (2,205 lb) of bombs, missiles, or rocket pods
The Yak-38 was not a successful aircraft and was hampered by its limited range, payload, and performance. It saw limited use in the Soviet Navy and was retired from service in the 1990s.
7. Convair F-102 Delta Dagger – Not Quite Supersonic
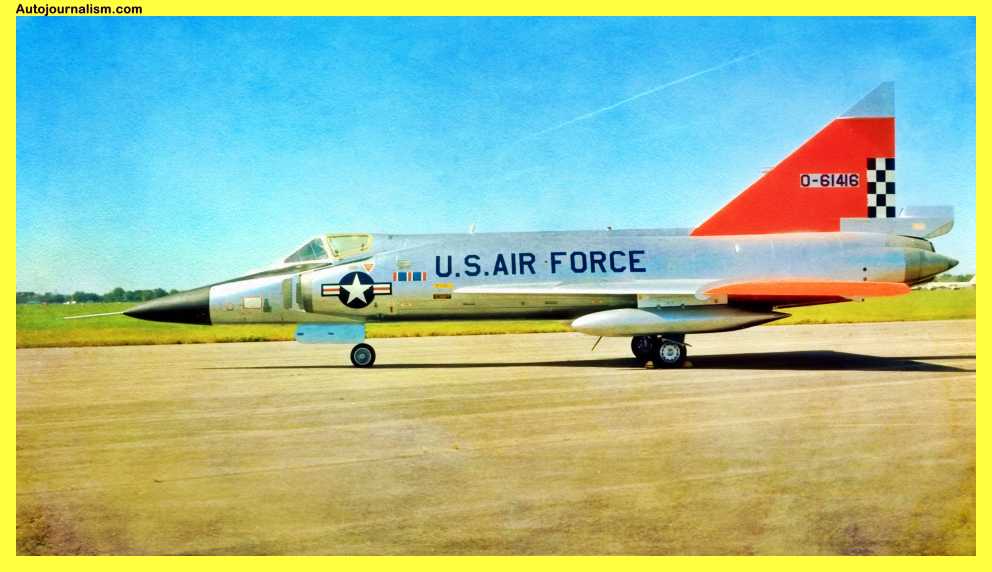

When the Cold War was at its height and the Soviet Union began launching long-range aircraft, the United States Air Force sought a new all-weather, high-altitude supersonic fighter. However, the nuclear weapons they initially acquired fell far short of the requirement, barely capable of reaching Mach 1.
Conveyor thought the f-102’s pure delta wing configuration best fit the high-performance requirements of the United States Air Force at the time, but despite the j57 engine’s early prototypes being unable to exceed Mach 1, the f-102 was plagued by a novel phenomenon known as transonic drag.
The Convair F-102 Delta Dagger was a supersonic interceptor aircraft developed for the United States Air Force (USAF) in the 1950s. It was designed to defend against enemy bombers and was equipped with radar and air-to-air missiles. Here are some key specifications for the F-102:
- Length: 55 ft 2 in (16.82 m)
- Wingspan: 38 ft 6 in (11.73 m)
- Height: 16 ft 2 in (4.93 m)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 29,600 lb (13,389 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney J57-P-25 turbojet, 10,000 lbf (44.5 kN) of thrust
- Maximum speed: 725 mph (1,168 km/h)
- Range: 1,500 mi (2,400 km)
- Service ceiling: 50,000 ft (15,240 m)
- Armament: 2 × AIM-4 Falcon air-to-air missiles, 1 × 20 mm M61 Vulcan cannon
It should be noted that the F-102 was not quite supersonic, with a maximum speed of just over 700 mph. It was also not very agile and was primarily used as a long-range interceptor. The F-102 was retired from active service in the 1970s but remained in use with the Air National Guard until the 1980s.
6. Heinkel He-162 – Plywood And Glue Construction For Home Builds
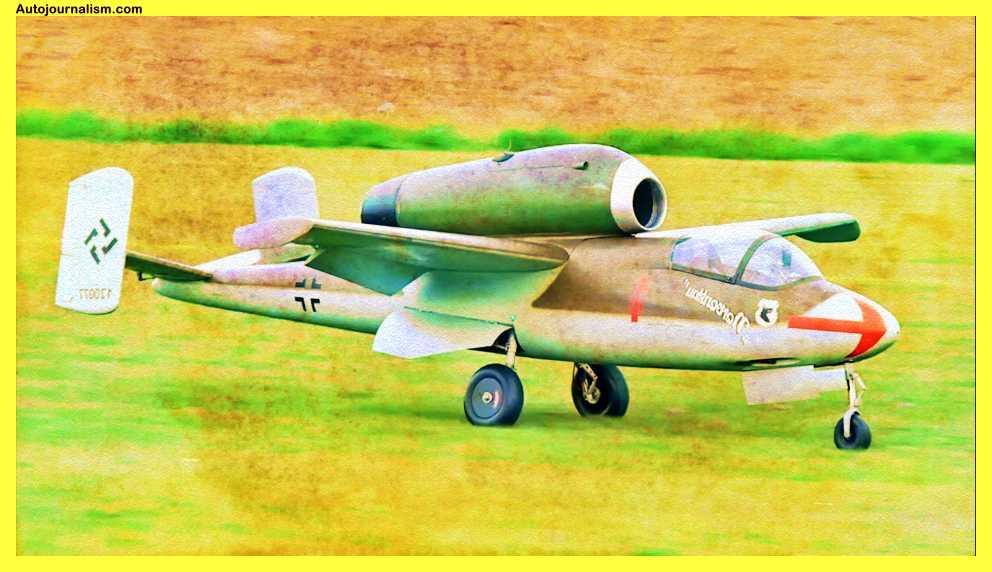

Due to the fact that much of the work on the Heinkel he-162 was done by regular people, Germany began producing it in 1943 when it ran out of combat aircraft. The he-162 was primarily constructed out of wood and utilized components from other aircraft, earning it the nickname “The People’s fighter.”
One of the fastest planes of World War II, the simple wood and glue construction of the hu-162 proved to be a fatal defect as the glue frequently corroded the airframe and caused crashes. It used a single BMW 003 turbojet and could travel over 550 miles per hour.
The Heinkel He-162 was a German jet-powered fighter aircraft developed during World War II. It was designed as a cheap and simple aircraft that could be quickly produced in large numbers, and was made largely of wood and glue to save on resources. Here are some key specifications for the He-162:
- Length: 9.50 m (31 ft 2 in)
- Wingspan: 7.00 m (23 ft 0 in)
- Height: 2.60 m (8 ft 6 in)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 2,800 kg (6,173 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Junkers Jumo 004B-1 turbojet, 8.83 kN (1,986 lbf) of thrust
- Maximum speed: 746 km/h (464 mph)
- Range: 400 km (249 mi)
- Service ceiling: 13,000 m (42,651 ft)
- Armament: 2 × 30 mm (1.18 in) MK 108 cannon, mounted in the nose
The He-162 was not a particularly successful aircraft, as it was rushed into production before it was fully developed. It saw limited use in the final months of World War II, and was not a significant factor in the outcome of the war.
5. Vought F7U Cutlass – Underpowered And Unreliable
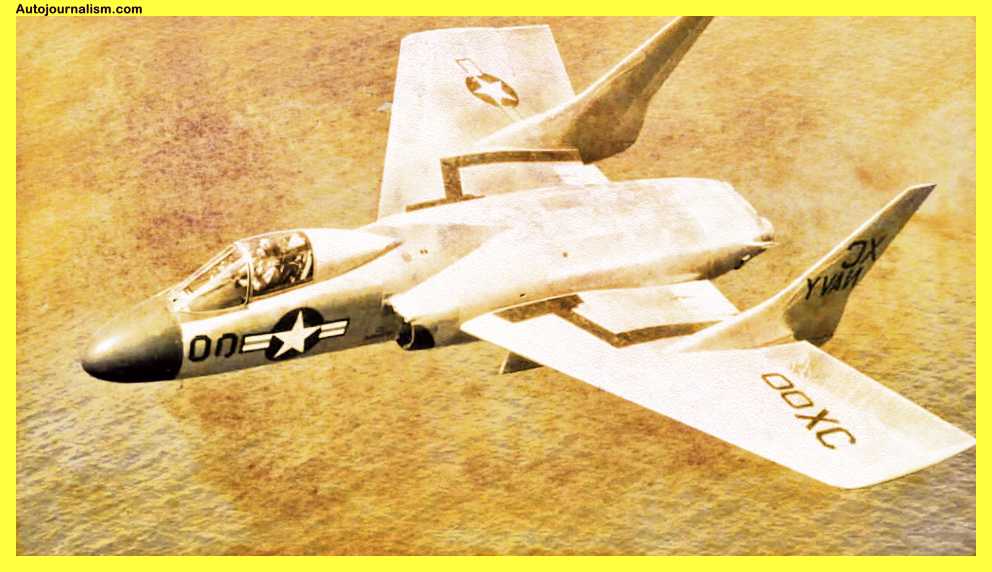

The Vought F7U Cutlass was designed for the US Navy, but it’s difficult to imagine how Vought anticipated carrier deployments would proceed. In contrast to other nations’ sleek jet fighters, the F70 Cutlass had an oddly raised nose. This was because its landing gear was so complicated and unreliable that it frequently broke when it touched down on a carrier deck. By far the biggest issue with the Watts F7U was how frequently it broke down. The Westinghouse J46 engines frequently got stuck.
The Vought F7U Cutlass was a carrier-based jet fighter aircraft developed for the United States Navy (USN) in the 1950s. It was known for its unusual tailless delta wing design, but was plagued by problems with its engines and systems, which made it underpowered and unreliable. Here are some key specifications for the F7U:
- Length: 46 ft 7 in (14.20 m)
- Wingspan: 35 ft 0 in (10.67 m)
- Height: 13 ft 8 in (4.17 m)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 23,500 lb (10,660 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × Westinghouse J34-WE-32/34 turbojets, 3,700 lbf (16.4 kN) each
- Maximum speed: 656 mph (1,057 km/h)
- Range: 1,100 mi (1,770 km)
- Service ceiling: 50,000 ft (15,240 m)
- Armament: 4 × 20 mm (0.79 in) Mk 12 cannon, up to 2,000 lb (910 kg) of bombs, missiles, or rocket pods
The F7U was not a successful aircraft, and only a small number were built. It was retired from active service in the mid-1950s, after only a few years of service.
4. Bell P-59 Airacomet – Slower Than Piston Aircraft It Replaced
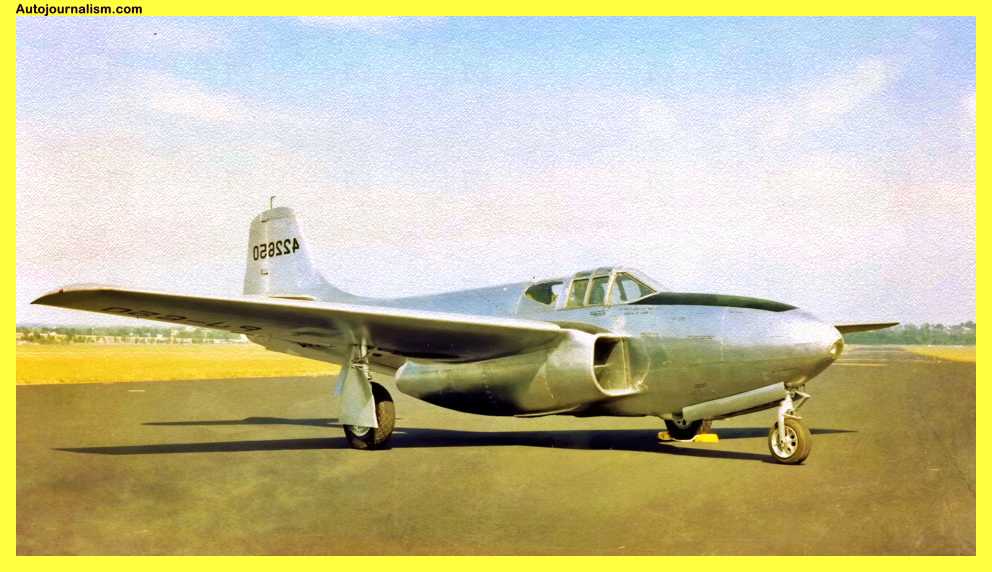

Even though you would think that jets are meant to be quick, the USAF’s first operational jet fighter, the Bell p59, couldn’t keep up with piston-engined aircraft with a top speed of only 413 miles per hour. The general electric j31 engine, which was primarily based on a British engine but lacked sufficient power, was the only issue. Failure to meet the performance requirements of the US military would have a significant impact on production numbers; for instance, the US Army canceled more than half of its allotment as a result.
The Bell P-59 Airacomet was the first jet-powered aircraft developed for the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF). It was developed during World War II and was intended to replace the piston-engined fighters of the time. However, it was slower than many of the aircraft it was intended to replace and was not very successful. Here are some key specifications for the P-59:
- Length: 36 ft 3 in (11.05 m)
- Wingspan: 38 ft 10 in (11.84 m)
- Height: 10 ft 10 in (3.30 m)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 7,300 lb (3,311 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × General Electric I-A turbojet, 1,650 lbf (7.3 kN) of thrust
- Maximum speed: 407 mph (655 km/h)
- Range: 1,000 mi (1,609 km)
- Service ceiling: 45,000 ft (13,716 m)
- Armament: None (originally intended to carry 2 × 20 mm (0.79 in) cannon, but these were not fitted on production aircraft)
The P-59 was not a successful aircraft, and only a small number were built. It was used for training and research purposes but did not see combat during World War II. It was retired from service in the 1950s.
3. De Havilland Sea Vixen – Accidents Accounted For 38% Of All Aircraft
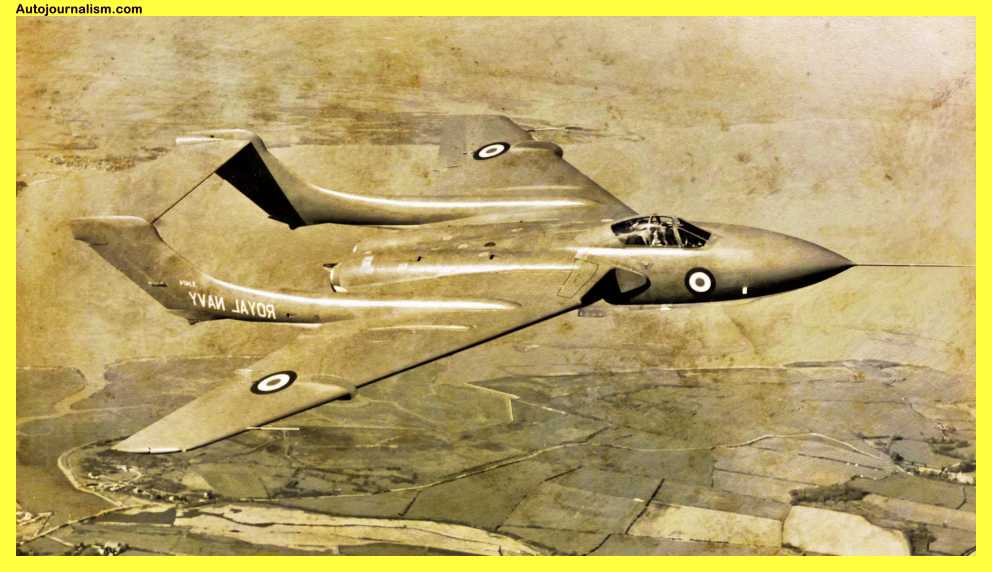
The Royal Navy continued to use the odd sea Vixen as its fixed-wing carrier-based aircraft until 1972, despite the necessity for the far better F4 Phantom. This was in spite of the fact that the F4 Phantom required a peculiar twin-boom to-engine plane with an off-center cockpit for the pilot, which can only make it harder to fly. This type is renowned for being difficult to control, and 55 145c Vixens were lost in accidents rather than being destroyed in battle starting in 1951.
The De Havilland Sea Vixen was a British carrier-based jet fighter aircraft developed in the 1950s. It was used by the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force and was known for its distinctive twin-boom tail design. Here are some key specifications for the Sea Vixen:
- Length: 46 ft 4 in (14.12 m)
- Wingspan: 38 ft 0 in (11.58 m)
- Height: 14 ft 6 in (4.42 m)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 28,000 lb (12,700 kg)
- Powerplant: 2 × de Havilland Ghost 50 Mk.1/2 turbojets, 7,000 lbf (31 kN) each
- Maximum speed: 710 mph (1,140 km/h)
- Range: 1,000 mi (1,609 km)
- Service ceiling: 45,000 ft (13,716 m)
- Armament: 4 × 30 mm (1.18 in) ADEN cannon, up to 6,000 lb (2,722 kg) of bombs, missiles, or rocket pods
It should be noted that the Sea Vixen had a high accident rate, with 38% of all aircraft being lost in accidents. This was due in part to the aircraft’s complexity and the challenges of operating from aircraft carriers. The Sea Vixen retired from active service in the 1970s.
2. Mikoyan Gurevich Mig-23 – Still In Service 50 Years Later
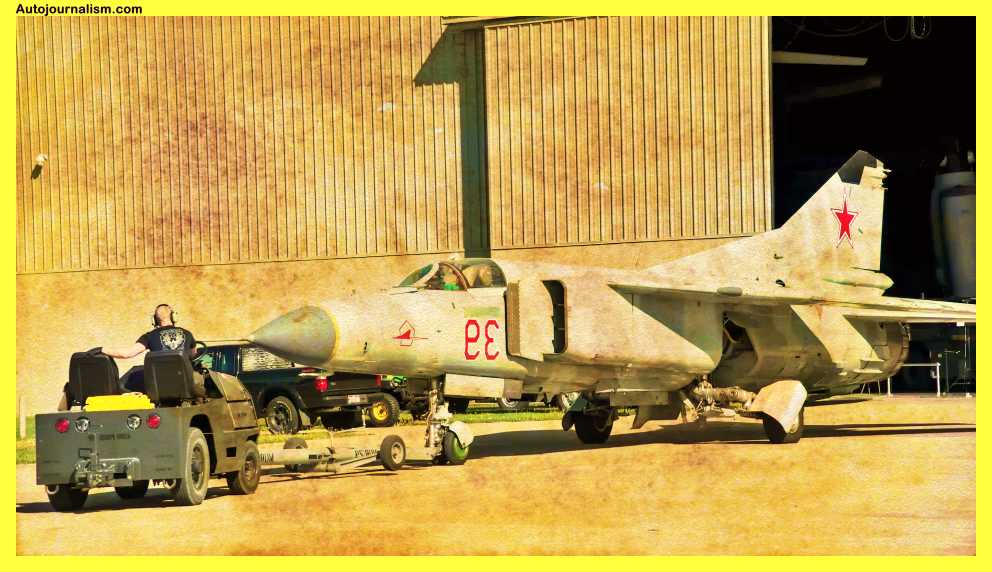

The MIG-23 vlogger, which first flew in 1967 and soon became a significant seller for the Mikoyan Gurevich, the world’s quickest combat aircraft, followed the deadly MIG-25 fox bat three years after it was introduced. It has now found homes with over three international operators. its ground-breaking changeable geometry Due to its high cost, poor quality, build, and strength, the MIG-23 was one of the least dependable and labor-intensive fighters of the Cold War era. Wing structure allowed the best low-speed stability as well as high-speed performance above 1,500 miles per hour.
The Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 (NATO reporting name: “Flogger”) is a Soviet-designed fighter aircraft that was developed in the 1960s. It was a multirole aircraft that was used for air-to-air and air-to-ground missions and was known for its swing-wing design that allowed it to adjust its wing sweep angle for different flight regimes. Here are some key specifications for the MiG-23:
- Length: 17.32 m (56 ft 10 in)
- Wingspan: 9.50 m (31 ft 2 in) (fully extended), 6.98 m (22 ft 11 in) (fully swept)
- Height: 4.70 m (15 ft 5 in)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 18,000 kg (39,683 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Tumansky R-27F-300 afterburning turbofan, 8,300 kgf (81.6 kN, 18,300 lbf) of thrust
- Maximum speed: 2,335 km/h (1,450 mph)
- Range: 1,250 km (777 mi)
- Service ceiling: 17,500 m (57,415 ft)
- Armament: 1 × GSh-23L cannon, up to 6,000 kg (13,227 lb) of bombs, missiles, or rocket pods
The MiG-23 was widely exported and used by numerous countries around the world. It is still in service in some countries 50 years after it was first introduced.
1. Lockheed F-35 Lightning II – Failed To Meet Its Original Design Criteria
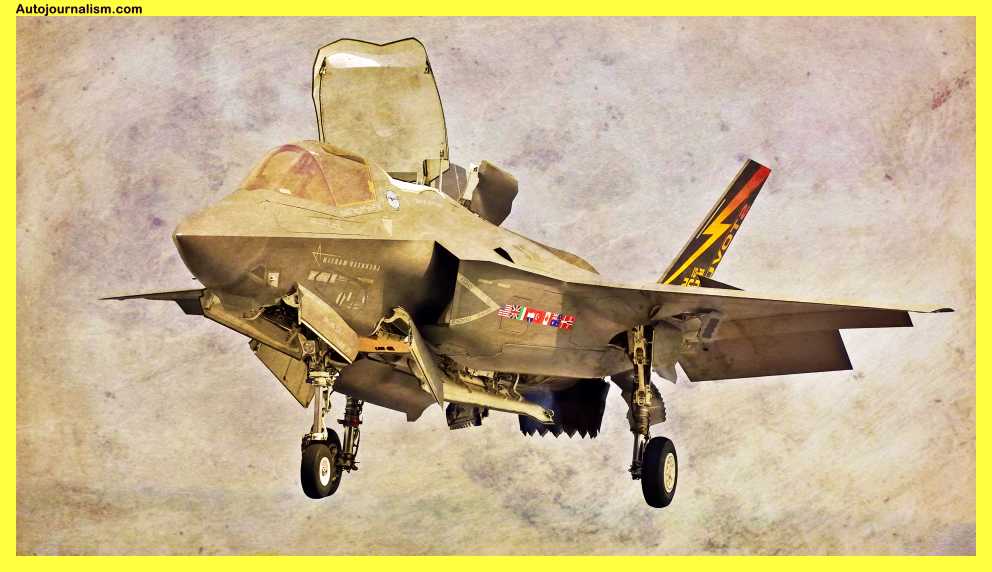

Due to these demanding operating requirements, the Lockheed F-35 Lightning II is without a doubt the most technologically advanced aircraft to ever take to the air, integrating and replacing numerous previous aircraft in the process. The F-35 program was designed to be the most technologically advanced and capable fighter in the world, therefore it came as a shock when high-ranking USAF Chiefs declared it a failure because it was too complicated and expensive. Worse is yet to come.
The Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II is a fifth-generation, single-seat, single-engine, stealthy multi-role fighter aircraft developed for the United States and its allies. It was designed to perform a variety of missions, including air superiority, ground attack, and electronic warfare. Here are some key specifications for the F-35:
- Length: 51 ft 3 in (15.62 m)
- Wingspan: 35 ft 4 in (10.77 m)
- Height: 14 ft 6 in (4.42 m)
- Maximum takeoff weight: 70,000 lb (31,800 kg)
- Powerplant: 1 × Pratt & Whitney F135 afterburning turbofan, 40,000 lbf (180 kN) of thrust
- Maximum speed: 1,200 mph (1,931 km/h)
- Range: 2,200 mi (3,500 km)
- Service ceiling: 50,000 ft (15,240 m)
- Armament: 1 × 25 mm GAU-22/A cannon, up to 18,000 lb (8,165 kg) of bombs, missiles, or rocket pods
It should be noted that the F-35 has faced numerous problems and cost overruns during its development and production, and has failed to meet many of its original design criteria. Despite this, it has been procured by a number of countries and is currently in service with several militaries around the world.
Also Check: