Top 10 Light Combat Helicopter In The World ( LCH )
Table of Contents
Recently the Government of India has approved 15 Indian-made helicopters for the army. Today we will talk about HAL Light Combat Helicopter or LCH. Hindustan Aeronautics Limited’s Light Combat Helicopter (LCH) is a multi-role assault helicopter designed and manufactured in India. HAL openly declared in 2006 that they were developing a light combat helicopter. In January of that year, the LCH completed initial ground tests followed by its first flight test in March 2010. The LCH has the highest flight ceiling among all attack helicopters and is equipped to carry out high-altitude missions.
Note: This is not a comparison or a complete list, and it may change at any time. However, I can promise you that these are all Light Combat Helicopters WOTH the correct information, which you will not find on Wikipedia or other websites, or even on the entire Internet in one place. Furthermore, you will receive more than 10 LCH from this article.
LCH Full Form: Light Combat Helicopter
HAL Full Form: Hindustan Aeronautics Limited
List of Top 10 Light Combat Helicopter In The World ( LCH )
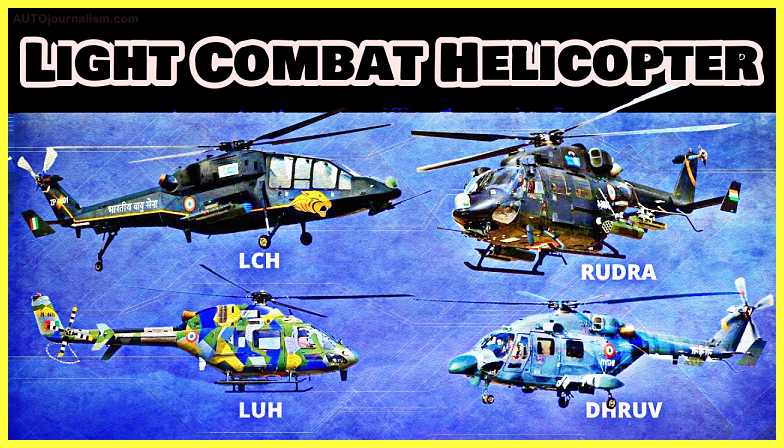
1. HAL DHRUV ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
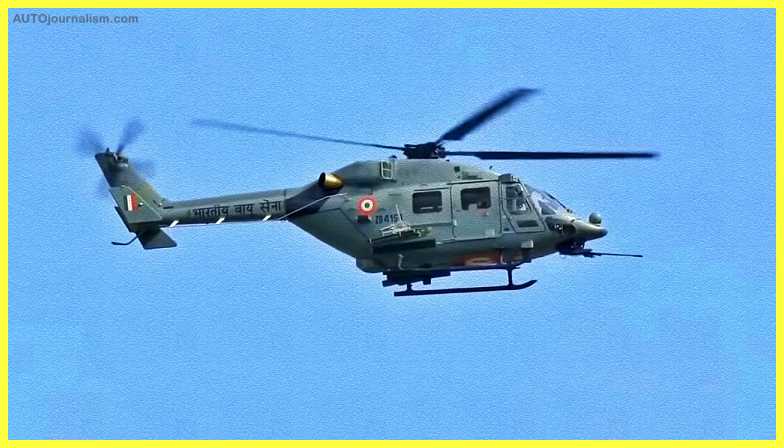

The Dhruv (Pole Star) Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH) was developed in-house by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited’s Helicopter Division (HAL). It is a light (5.5t class) multirole and multimission helicopter designed for Army, Air Force, Navy, Coast Guard, and civilian missions in both day and night utility and attack duties. In 2000, the helicopter, which was designed to FAR 29 criteria, went into series production. Dhruv MK-I, MK-II, MK-III, and MK-IV, or Weapon System Integrated, are the four major variations (WSI). As of March 2017, HAL had produced 228 Dhruv helicopters, with 216 in service with the Indian Armed Forces.
2. HAL LCH ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
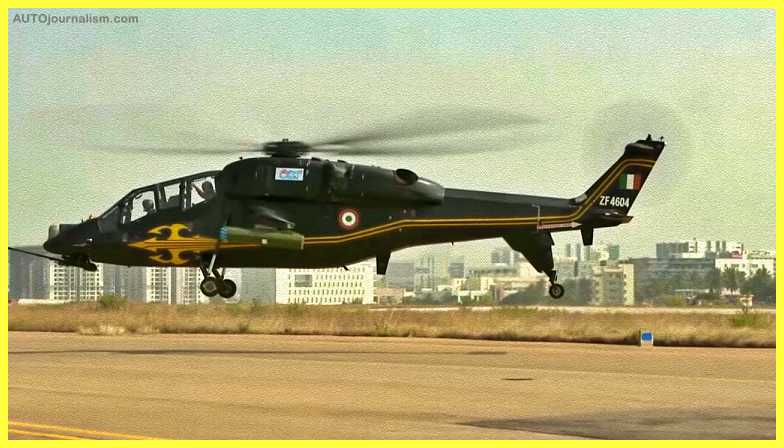

Hindustan Aeronautical Limited designed and produced the light combat helicopter (LCH) (HAL). It’s an attack helicopter that’s based on the existing Dhruv. The LCH can be used for a variety of missions, including scouting, insurgency, damaging enemy defenses, search and rescue, anti-tank, and scouting. Throughout the network, a datalink system provides mission data to mobile platforms and ground stations. The LCH was designed to satisfy the needs of the Indian Air Force and Indian Army, which have each bought 62 and 114 units. In March 2010, it took off for the first time from Bangalore.
3. HAL RUDRA ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
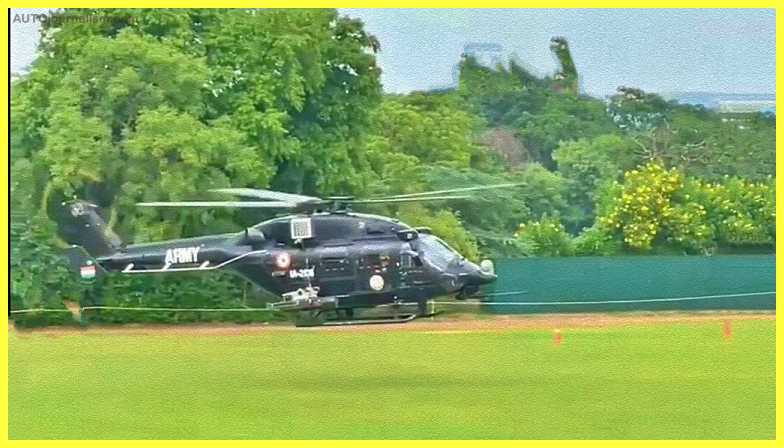

Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) produces the Rudra attack helicopter for the Indian Army. It’s the Dhruv Advanced Light Helicopter’s Weapon System Integrated (WSI) Mk-IV variant (ALH). Rudra is the first weaponized helicopter developed in the country. The HAL Rudra helicopter can undertake reconnaissance, troop transport, anti-tank warfare, and close air support, to name a few tasks. HAL has been contracted by the Indian Army and Air Force to build 76 Rudra ALH Mk-IV helicopters. The Indian Army plans to supply the Army Aviation Corps with 60 helicopters distributed into six squadrons. The Indian Army received the first Rudra helicopter from HAL in February 2013.
4. HAL LUH ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
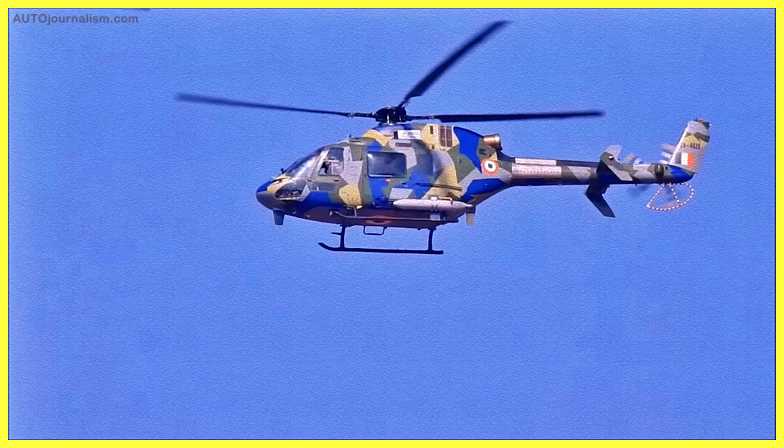

The LUH is being conceived and developed as a replacement for the Indian Armed Forces’ Cheetah and Chetak helicopters. The LUH is a new generation 3-ton helicopter with cutting-edge technology such as a Glass cockpit with Multi-Function Displays (MFD) and is powered by a single Turbo Shaft engine with enough power margin to handle demanding high-altitude missions. In the future decades, LUH will address the expanding needs of this class of helicopters. The helicopter will have a top speed of 220 km/h, a service ceiling of 6.5 km, and a range of 350 km with a payload of 500 kg.
5. HAL CHETAK ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
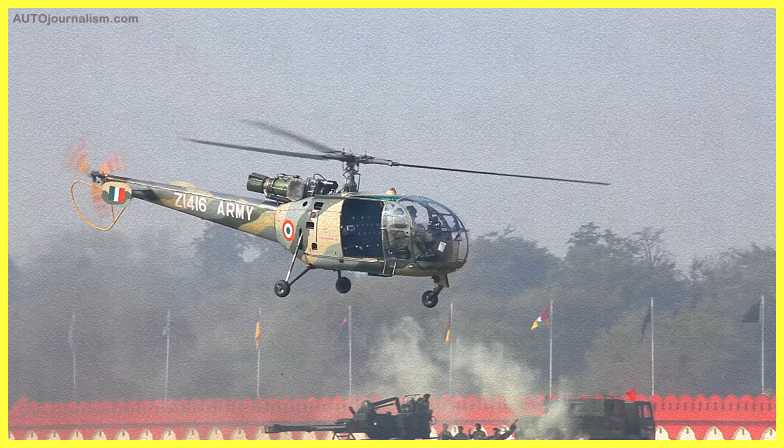

HAL’s Helicopter Division began producing helicopters in 1962 when it signed a contract with M/s SUD-AVIATION (now M/s AIRBUS (Former EUROCOPTER), France) to produce Alouette III helicopters (Chetak). In 1965, the first Chetak (Alouette III) was delivered in ‘Fly Away’ condition. The Chetak helicopter is a helicopter of the two-ton class. The Chetak helicopter has seven seats and is multifunctional, multi-role, multi-purpose, and capacious. The Artouste – III B turboshaft engine powers the helicopter.
Commuting, cargo/material transport, casualty evacuation, Search & Rescue (SAR), Aerial Survey & Patrolling, Emergency Medical Services, Off-shore operations, and Underslung activities are all possible with the helicopter. HAL has developed and sold over 350 of these versatile helicopters, which are currently in service in India and overseas. MOD Namibia and MoD Suriname have recently placed orders for Chetak helicopters with HAL.
6. Agusta A129 Mangusta (Italy) ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
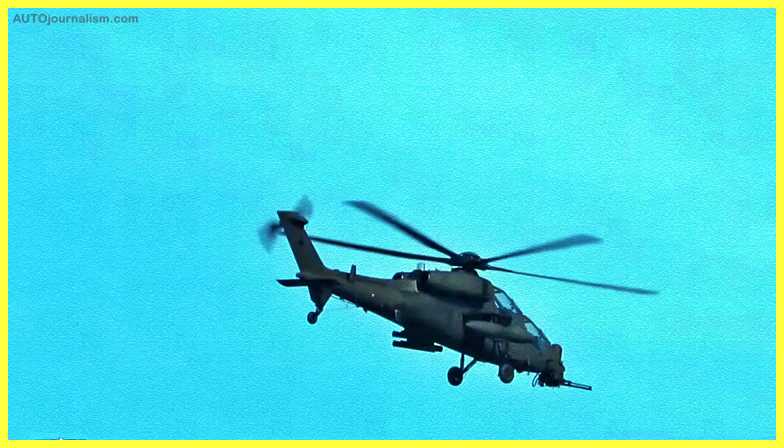

The Mangusta A129 was the first dedicated attack helicopter built in Western Europe. In 1990, the Italian Army received the first helicopters. With the conclusion of the Cold War, Mangusta production was halted in 1992 due to funding issues and changing operational needs. Later, all Mangustas in Italy were updated to meet the A129 International standard.
7. TAI/AgustaWestland T129 ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
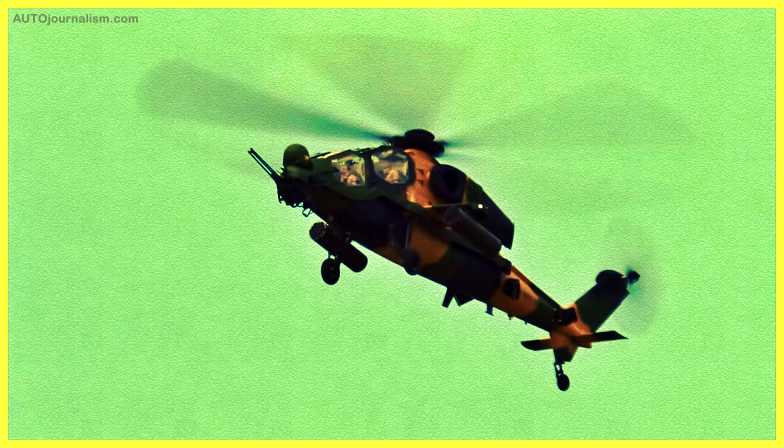

The TAI/AgustaWestland T129 ATAK is a multi-role, all-weather attack helicopter with two engines and tandem seats based on the Agusta A129 Mangusta chassis. Turkish Aerospace Industries collaborated with Agusta Westland to build the T129. The helicopter is developed for sophisticated assault and reconnaissance missions in both day and night settings in hot and high regions with rugged terrain.
The Turkish Armed Forces needed an attack and tactical reconnaissance helicopter, hence the ATAK program was started. The T129 is the product of Turkish-developed avionics, airframe upgrades, and weapon systems being integrated into the AgustaWestland A129 airframe, together with updated engines, transmissions, and rotor blades. The Turkish Army and other services, such as the Turkish Gendarmerie, employ it.
8. CAIC Z-10 ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
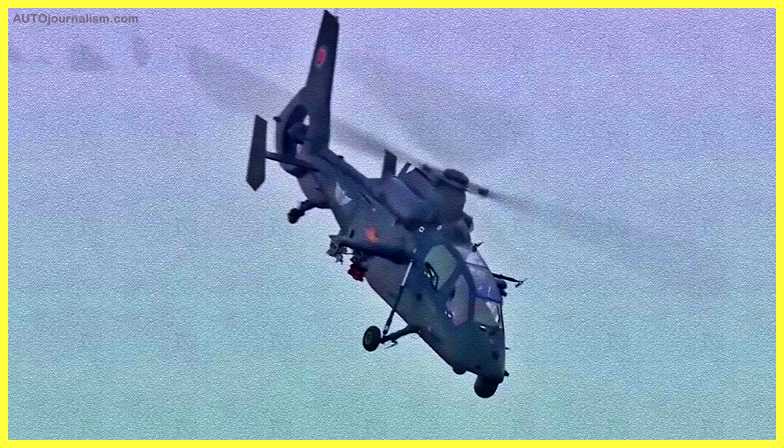

(China) The Chinese Z-10 is the country’s first dedicated assault helicopter. Eurocopter and Augusta provided considerable technological assistance in the development of the aircraft. According to some reports, the Russian Kamov helicopter design bureau contributed to the development of this attack helicopter. Anti-armor and battlefield interdiction are the primary goals of the Z-10. It has the ability to engage in limited air-to-air combat as well.
9. Denel AH-2 Rooivalk (South Africa) ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
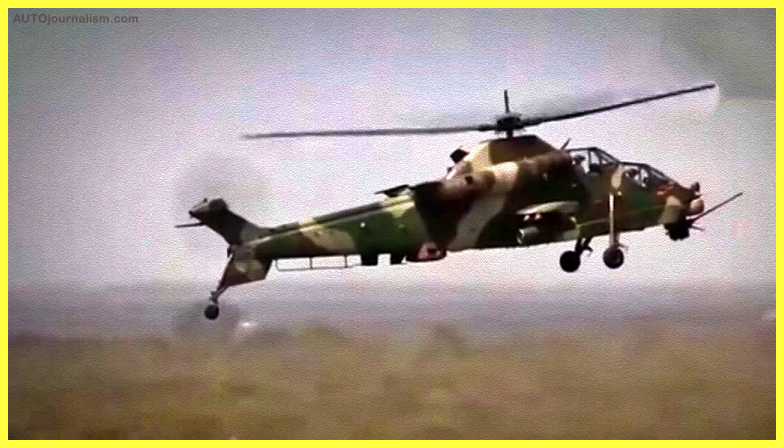

In the South African Air Force, the Denel AH-2 Rooivalk is an important attack helicopter. It was released in 2011. The attack plane is armed with a 20 mm cannon and is capable of carrying air-to-air missiles, anti-armor missiles, and unguided rockets. It also has a target acquisition system and a sophisticated navigation system. GPS, infrared, and Doppler radar systems are all used. It is regarded as one of the world’s best attack helicopters. Other countries’ air forces also utilize this gunship.
10. Eurocopter Tiger (Multinational)( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
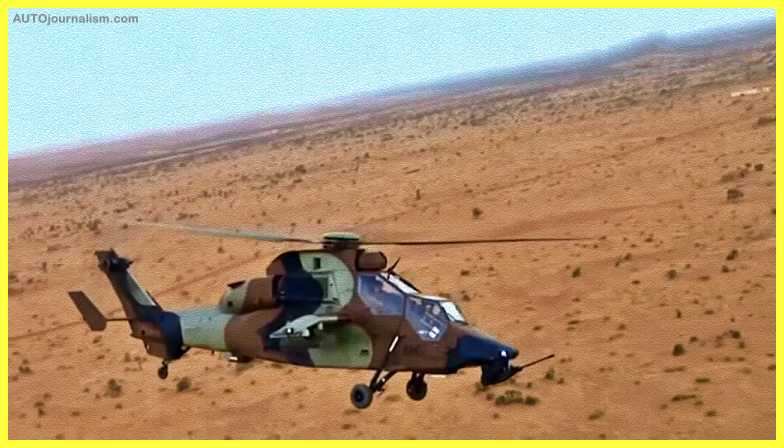

France and Germany collaborated on the Eurocopter Tiger. It’s a medium-weight assault helicopter that first saw action in 2002. Australia and Spain are among the countries that use it. The Tiger has fought in Afghanistan, Libya, and Mali.
11. Harbin Z-19 ( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
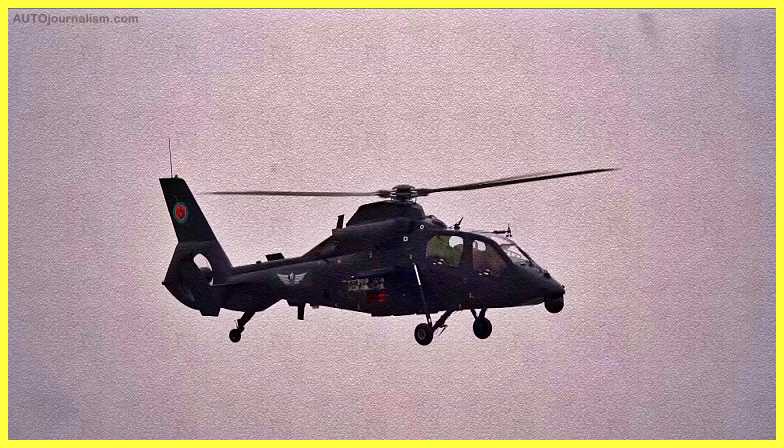

Harbin Aircraft Industry Group (HAIG) developed and constructed the Z-19 light attack and reconnaissance helicopter for the People’s Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF).
Changhe Aircraft Industry Group (CAIG) of China designed and constructed this triple-engine multi-role helicopter. The Z-19 light attack and reconnaissance helicopter has a stealthy design that includes a reduced forward fuselage and a tandem cockpit. It also has a minimal acoustic signature and is capable of performing operations in adverse weather and environmental situations.
12. Kamov Ka-52 (Russia)( Best Light Combat Helicopter )
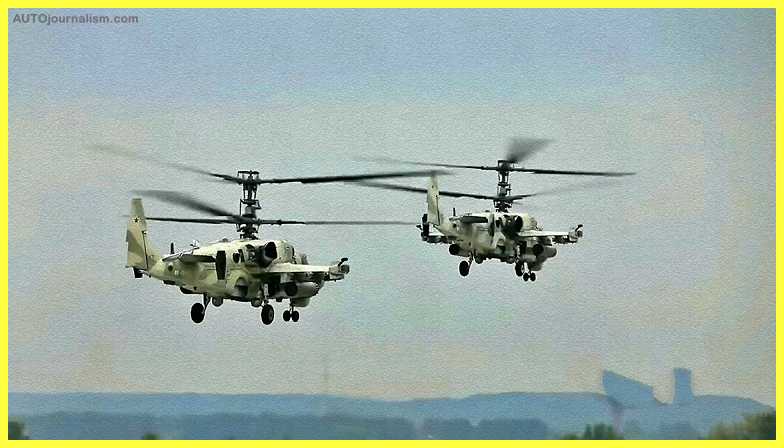

The Ka-52 is a development of the Ka-50 and a two-seat version of it. This assault helicopter was first used by the Russian Army in 2008, and small-scale manufacturing began in 2009. Because of its two coaxial contra-rotating main rotors, the Ka-52 is one of the fastest and most nimble attack helicopters. This gunship’s armor can withstand projectiles with a diameter of 23 mm. Ejection seats are used by pilots.
The fuselage houses a four-bladed main rotor with a diameter of 11.9m, as well as a fenestron tail rotor and two stubby wings. Non-retractable front landing gears are also installed on the fuselage for safe takeoff and landing. The helicopter has a length of 12 meters and a height of 4.01 meters. The empty weight is 2,350kg, while the maximum take-off weight is 4,500kg. The helicopter is operated by a two-person crew. This includes the pilot, who sits in the front of the cockpit, and the gunner, who sits in the back. The cockpit is equipped with crash-resistant seats and armor panels to protect the crew. For defense against infrared-guided attacks, an infrared-suppressing exhaust system is also installed.
Here is the list of all Major features of the HAL Helicopter ( Made in India ):
Hindustan Aeronautics HAL LIGHT COMBAT HELICOPTER
1. Glass cockpit
2. Integrated architecture and display system
3. Digital camouflage System
4. Crashworthy bottom structure
5. Crashworthy fixed tricycle landing gear
6. Crashworthy self-sealing fuel tanks
7. Armor protection
8. Infrared suppressor connected to the engine exhaust
9. Canted flat panels for low radar cross-section
10. Integrated dynamic system
11. Hingeless main Rotor
12. Bearing-less tail Rotor
13. Anti-resonance Isolation System
Light Combat Helicopter UPSC ( LCH Points for UPSC Students )
- The Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) on Wednesday (March 30) approved the procurement of 15 indigenously developed Light Combat Helicopters (LCH),
- At a cost of Rs 3,887 cr along with infrastructure sanctions worth Rs 377 cr.
- The decision was taken at a meeting chaired by Prime Minister Narendra Modi.
- The LCH’s origins can be traced back to the 1999 Kargil conflict when the Indian Army and Air Force realized they needed an attack helicopter that could fly at ultra-high altitudes (LAF).
- The infiltrating Pakistan Army troops had occupied several heights on the Indian side of the Line of Control, but the Indian military’s current Russian-made assault helicopters lacked the operational ceiling that would have allowed them to deploy at those heights.
- Against those heights, the IAF was compelled to utilize MI-17 helicopters in a modified capacity, and one helicopter was lost when it was shot upon by the enemy.
- It was in 2006 that Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) announced its intention to develop an LCH that could operate in the harsh desert conditions as well as the high altitude areas of Ladakh including the Siachen Glacier.
- In February 2010, the first ground run of the LCH prototype took performed, followed by the first flying test of the helicopter a month later.
- Modifications were made to this prototype and the subsequent version was made public at the Aero India 2011 in February, and in June of that year, the flight test of the second prototype took place. A third prototype was further tested in November 2014 with integrated weapon platforms and sensors.
- This version was a considerably improved one with lighter weight and advanced configurations.
- In the coming year, further hot weather and cold weather tests were done on the helicopter in Rajasthan and Ladakh and a fourth prototype was tested in November 2015.
- After all, systems had been properly integrated and tested for performance, HAL gave the go-ahead for the helicopter’s operational deployment in January 2019.
- The LCH production hangar at HAL Bengaluru was inaugurated by the Defence Minister in February 2020. The production line, according to reports, can create up to 30 helicopters every year.
Feature of LCH
- According to HAL, the LCH has “the maximum possible commonality with Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH”.
- The assault helicopter has a tandem cockpit with a pilot and co-pilot (one behind the other).
- The helicopter is equipped with stealth features such as armor, night assault capability, and crash-worthy landing gear to improve its survivability.
- It has a maximum take-off weight of 5,800 kg and is powered by two Shakti engines. It has a range of 550 kilometers and an operational ceiling of 6.5 kilometers, with a top speed of 268 kilometers per hour.
- LCH carries a 20 mm gun and 70 mm rockets, as well as air-to-air and air-to-ground missiles. The LCH has a full glass cockpit, an Electronic Warfare suite, and a helmet-mounted display for the pilots.
Role of LCH
- The LCH is particularly suited to the anti-tank role, as it can fly low and quickly to strike and destroy opposing armor columns.
- As per HAL, it is also suitable for the scout role wherein it can fly ahead of advancing columns of the Army and detect enemy presence.
- It is also suitable for air defense roles and the destruction of enemy air defense assets.
- It’s also suitable for urban warfare and combat search and rescue missions.
More info about the LCH, HAL LIGHT COMBAT HELICOPTER
LCH Specification
LCH has a tandem cockpit to accommodate a pilot and co-pilot or gunner. It measures 15.8 m long, 4.70 m in height with 4.7 m wingspans. The maximum take of weight is 5,800kg including 700 kg of payload. LCH is powered by two HAL Turbomeca Shakti-1H1 turboshaft engines, each engine produces a maximum output power of 1,032 kW or 1,384 hp, and it features a Full Authority Digital Electronic Control system. Maximum speed and Never exceed the speed of LCH are 268 km/h and 330 km/h respectively with an endurance of 3 hours 10 minutes. LCH has a maximum range of 500km with full payload and the ferry range is 700 km. LCH can operate at a maximum altitude of 21,300ft with a full payload.
LCH Armament
LCH has 20mm M621 cannon is combined with a Nexter THL 20 turret and integrated into a helmet-mounted sight. The LCH features four hardpoints, two on each wing, from which it may launch rockets, air-to-air missiles, anti-tank guided missiles, and bombs. It has the capability of incorporating both foreign and Indian-made weapons. LCH can fire HELINA, Helicopter-launched Nag, Dhruvastra, and SANT or Standoff Anti-tank Guided Missile. Mistral air to air missile, 20 mm gun, and 70mm rocket-firing trials have been completed.
Missions
LCH can undertake a variety of attack tasks at any time of day or night, including anti-infantry, anti-armor, air defense against slow-moving aerial targets, including both manned and unmanned aerial vehicles, counter-insurgency operations, counter-surface force operations, and so on. The defeat of enemy air defense operations, urban warfare, escort to special heliborne operations, support of combat search and rescue operations, and armed aerial survey missions are all part of the job.
LCH Avionics
The LCH is equipped with state-of-the-art avionics that includes Elbit CoMPASS Onboard Sensor Suite, Electronic Warfare Suite, an integrated data link that enables network-centric warfare, and helmet-mounted sight. Bharat Electronics Limited manufactures the Elbit CoMPASS Onboard Sensor Suite. The suite includes a CCD camera, a forward-looking infrared imaging sensor, a laser rangefinder, and a laser designator for target designation in all weather, day, and night conditions. The Electronic Warfare Suite was developed by Saab Group, a South African company. A missile approach warning system, a radar warning receiver, and a laser warning receiver are all part of the package.
LCH Major features
The LCH is equipped with a glass cockpit, integrated architecture, and display system, digital camouflage system, crashworthy bottom structure, crashworthy fixed tricycle landing gear, crashworthy self-sealing fuel tanks, armor protection, For low radar cross-section, an infrared suppressor is attached to the engine exhaust, and the outside is covered by canted flat panels. The LCH also has an integrated dynamic system, which incorporates a hingeless main rotor and a bearing-less tail rotor, as well as an anti-resonance isolation system for vibration reduction.
Production
A total of 179 LCH are planned to be ordered, 114 for the Indian army and 65 for the Indian air force. LCH will be produced at HAL’s Helicopter Division, based in Bengaluru, and can deliver 30 helicopters per year.
NEXT TOPICS:
HAL HELICOPTERS,
HAL HELICOPTER PRICE,
HAL LUCKNOW,
HAL HELICOPTER LIST,
HAL TEJAS,
HAL BANGALORE,
HAL KANPUR,
HAL DHRUV,
HAL OFFICER LIST,
best light combat helicopter in the world,
best attack helicopter in the world 2022,
top 10 attack helicopters in the world 2022,
top 10 attack helicopters 2022,
best military helicopter in the world,
best helicopter in the world for private use,
light combat helicopter UPSC,
BEST LIGHT COMBAT helicopter in the world,
LIGHT COMBAT helicopter INDIA,
LIGHT COMBAT helicopter UPSC,
Hal light combat helicopter vs apache,
NEXT
Top 10 Future Weapons of Russia
Top 10 Hypersonic Missile In The World
Top 10 Future Weapons of Pakistan
Top 10 Ground Attack Aircraft in the World
Top 10 Best Tank Transporter In World
Top 10 ICBM Missiles in the World
Top 10 Longest Range Military Drone in The World (UAVs)
Top 10 Russian Fighter Jets ( All Sukhoi and MiG Jets )


